 SPICE Semantic Pseudo-labeling for Image Clustering
SPICE Semantic Pseudo-labeling for Image Clustering
# SPICE: Semantic Pseudo-labeling for Image Clustering
# 单位:Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
# 作者:Chuang Niu, Ge Wang
# 发表:Arxiv
# 摘要
However, these methods have limited performance when directly using the label features to measure the similarity among samples. This is because the category-level features lose too much instance-level information to accurately measure the relations of instances
SCAN [34] was proposed to leverage the embedding features of a representation learning model to search for similar samples across the whole dataset, and then courage the model to output the same labels for similar instances, achieving significantly better results.
However, the local nearest samples in the embedding space do not alwayshave the same semantics especially when the samples liearound the borderlines of different clusters as shown in Fig.1-(a) and (c), which may compromise the performance
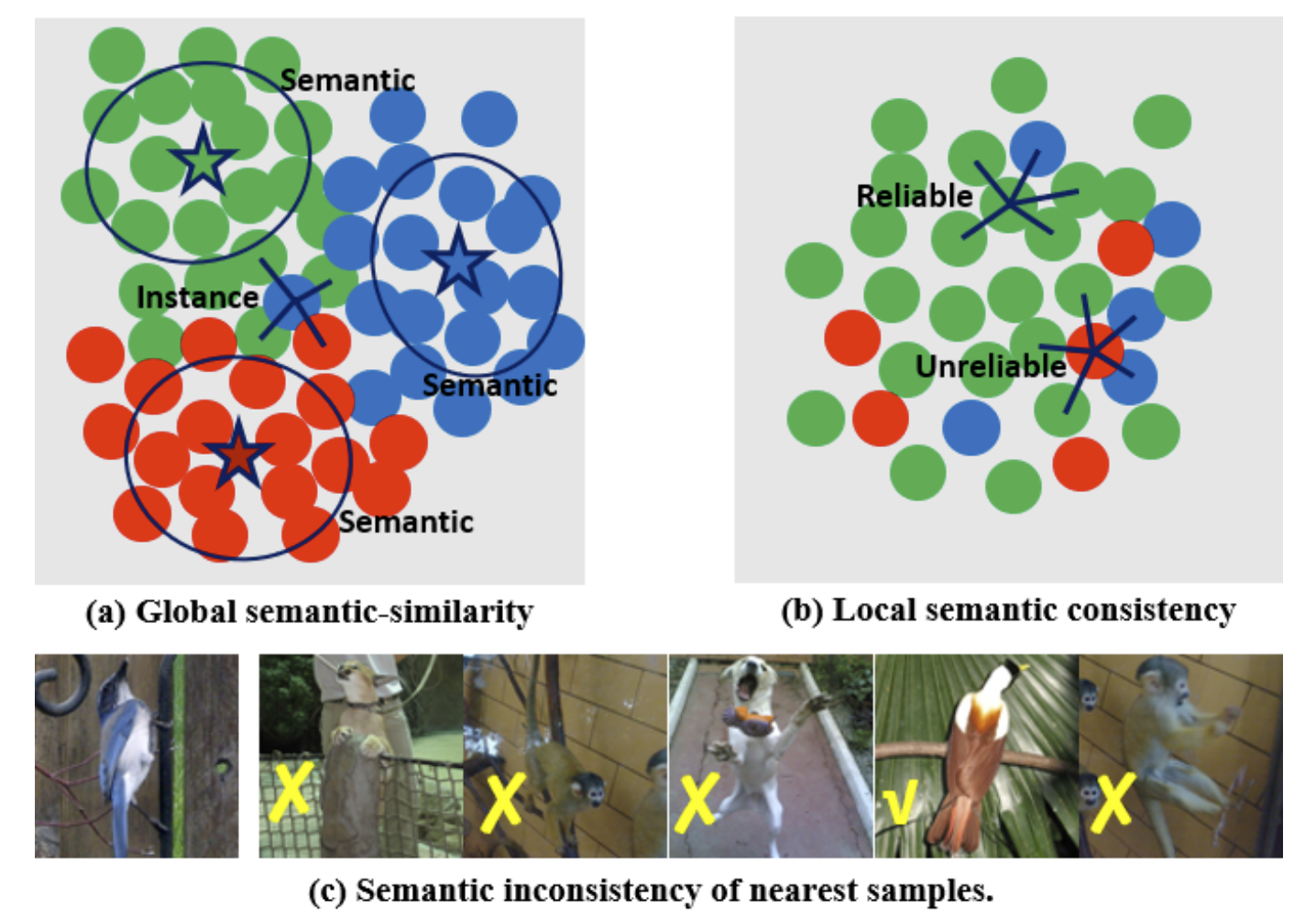
we call the similarity between the cluster prototype and instance samples as the semantic similarity,
To this end, we propose a semantic pseudo-labeling method that as-signs the same cluster label to semantically similar samples
Specifically, for each batch of samples, we use the most confident samples predicted by the classification model to compute the prototype of each cluster, and then spread thesemantic labels of prototypes to their neighbors based onthe semantic similarity.
Given these pseudo labels, the clas-sification model can be optimized using the classification loss directly, which is then used to compute prototypes in the next iteration.
To reduce the inconsistency of similar samples, we design a local consistency principle to select a set of reliably labeled images from the clustering results as in Fig. 1-(b), and thenreformulate the unsupervised task into a semi-supervisedpseudo-labeling process for performance boosting.
类的 prototype 如何计算?
- 使用分类模型最 confident 的样本
分类模型可以使用伪标签优化,在下一个 iteration 再来计算 prototype。
local consistency principle 来选择最可靠的标记图像。
SPICE framework that explicitly leverages both the
- discrepancy among semantic clusters
- the similarity among instance samples
- to adaptively label training samples in batch-wise.
Main Contributions:
- 使用 pseudo labels 以及 cls loss 来训练分类网络,利用语义类间的差异和样本实例间的相似性
- 提出新的 pseudo-labelding 方法来利用语义一致性,减小在 borderline 上的样本的语义不一致性
- 设计了 double softmax 交叉熵损失函数来让模型做出 confident 的预测,能够提升聚类的性能
- 设计了 local consistency principle 有效地减少 semantic inconsistency,将原始的聚类问题转化为半监督学习范式
- SPICE 在留个图像聚类的 benchmark 上达到了SOTA
Actually, these methods aim to train the classification model in the unsupervised setting while using multiple indirect loss functions, such as sample relations [5], invariant information [21, 27], mutual information [35], partition confidence maximisation [17], attention [28], and entropy[28, 17, 34, 27].
# 阅读
# 论文的目的及结论
# 论文的实验
用 MoCo-v2 来做表示学习
weak augmentation: Fixmatch 中的 flip-and-shift augmentation
strong augmentation:SCAN 中相同的策略
M 设置为1000,10个类别
m2 设置为 128
SPICE-self 有 10个 CLSHead, 性能最好的 head 会被选做最后的head
confident ratio 设置为 0.5
# 论文的方法
SPICE 框架分为三个主要的阶段
- 首先预训练一个无监督的表示模型,从 SCAN 中修改而来,接着该 CNN 冻结参数,在下面两个阶段提取embedding feature
- SPICE-Self 目标是基于无监督设置下提取的特征训练一个分类模型,SPICE-Slef 有三个分支
- 第一个分支将原始的图像作为输入,输出 embedding feature
- 第二个分支将weakly transformed 图像作为输入,预测语义标签
- 第三个分支将前两个分支的输出作为输入,使用基于语义相似性的 pseudo-labeling 算法生成伪标签,来用于第三个分支的监督信号
- SPICE-Self 只需要训分类模型的 light-weight classification head 即可
- SPICE-Semi 首先基于 SPICE-self 结果的局部语义一致性决定一个 reliably labeled set,就把聚类问题转化成半监督学习问题
SPICE-Self 算法

# 总结
# 论文的贡献
论文主要是针对弱监督语义分割提出了 Puzzle 模块,将原始图像分块后再算一个CAMs,并与原始的 CAMs 做一个重建损失,三项损失联合优化分类网络,提升 CAMs 的精度。
# 论文的不足
# 论文如何讲故事
# 参考资料
- https://paperswithcode.com/paper/spice-semantic-pseudo-labeling-for-image
- 02
- README 美化05-20
- 03
- 常见 Tricks 代码片段05-12
